Site-specific protein immobilization by fusion to self-labeling tags.
By A Mystery Man Writer
Last updated 17 Jun 2024

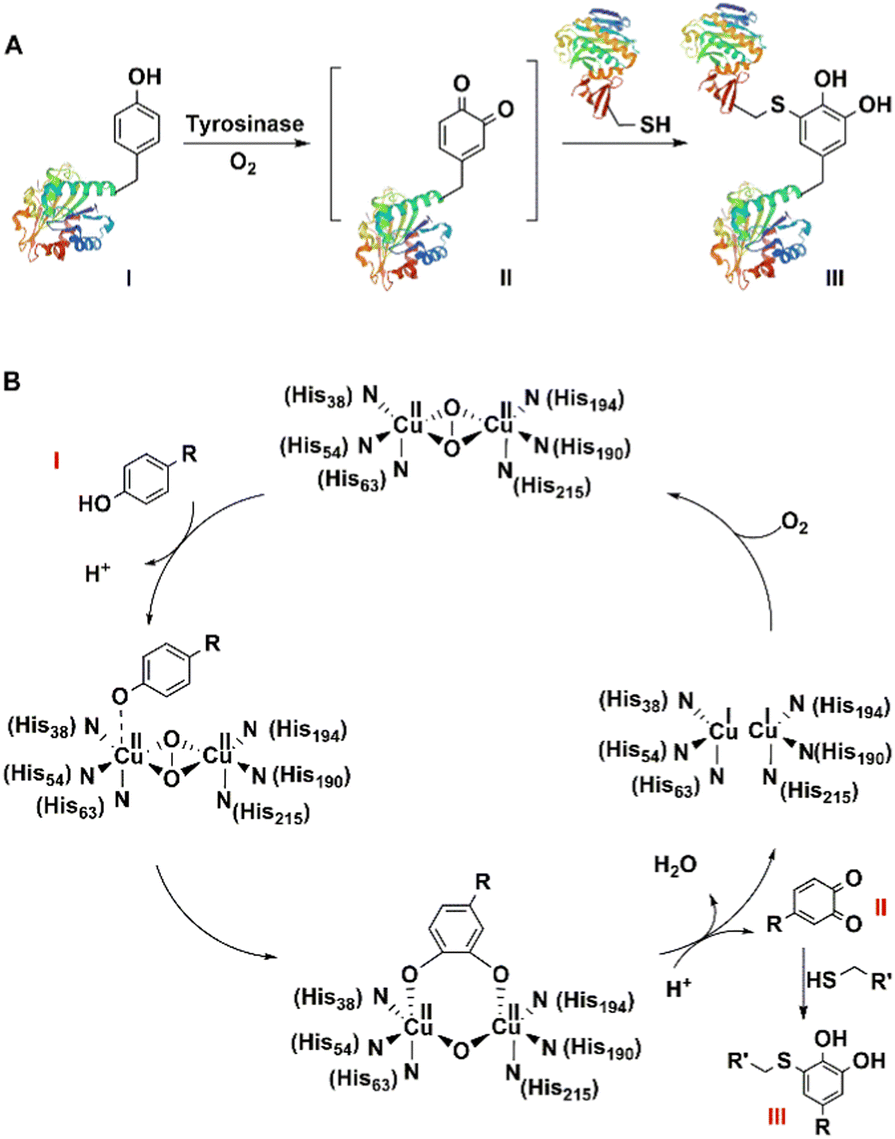
Download scientific diagram | Site-specific protein immobilization by fusion to self-labeling tags. (a) The SNAP-tag, 20 kDa in size, reacts with O 6 -benzylguanine. (b) The CLIP-tag (also 20 kDa) reacts with O 2 -benzylcytosine substrates, whereas the HaloTag (33 kDa) forms a covalent bond through nucleophilic displacement of halides from alkyl halide substrates. from publication: Recent advances in covalent, site-specific protein immobilization | The properties of biosensors, biomedical implants, and other materials based on immobilized proteins greatly depend on the method employed to couple the protein molecules to their solid support. Covalent, site-specific immobilization strategies are robust and can provide the | Immobilized Proteins, Protein Chemistry and Applied Microbiology | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Figure 1 from Snap-, CLIP- and Halo-Tag Labelling of Budding Yeast Cells
Putting precision and elegance in enzyme immobilisation with bio-orthogonal chemistry - Chemical Society Reviews (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1CS01004B

Site-Selective Protein Modification: From Functionalized Proteins to Functional Biomaterials - ScienceDirect

PDF) Recent advances in covalent, site-specific protein immobilization

Catalysts, Free Full-Text

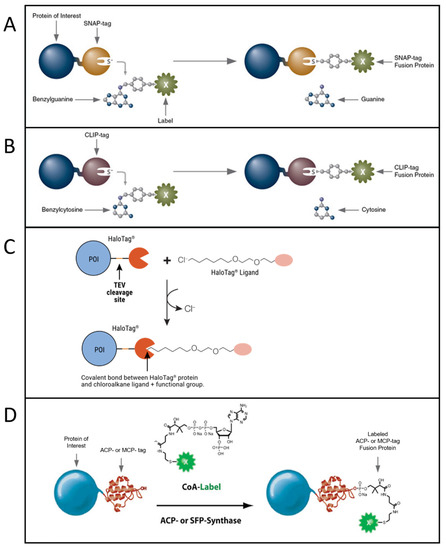
A) A protein of interest fused to an enzyme tag specifically binds to

Lipoic Acid Ligase A‐Mediated Ligation: Mechanism, Applications, and Emerging Innovations in Bioconjugation - Yamazaki - 2023 - ChemistrySelect - Wiley Online Library

Site-specific dual encoding and labeling of proteins via genetic code expansion - ScienceDirect

Protein Function Microarrays Based on Self‐Immobilizing and Self‐Labeling Fusion Proteins - Sielaff - 2006 - ChemBioChem - Wiley Online Library

Recent advances in covalent, site-specific protein immobilization. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Site-Specific Labeling of Endogenous Proteins Using CoLDR Chemistry
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Affinity Labels for Protein Purification

Sanne SCHOFFELEN, Senior Researcher
Recommended for you
-
 Wrapables Gold Foil Christmas Holiday Gift Tags/Kraft Paper Hang Tags for Gift-Wrapping, Labeling, Package Decoration (100pcs)17 Jun 2024
Wrapables Gold Foil Christmas Holiday Gift Tags/Kraft Paper Hang Tags for Gift-Wrapping, Labeling, Package Decoration (100pcs)17 Jun 2024 -
 LeadSeals 100 Plastic Tags Shipping Tags Water Proof Tags for Labeling Shipping Labels Security Seals Writable Marker Ties Hanging Tags Storage Tag17 Jun 2024
LeadSeals 100 Plastic Tags Shipping Tags Water Proof Tags for Labeling Shipping Labels Security Seals Writable Marker Ties Hanging Tags Storage Tag17 Jun 2024 -
 Thyle 500 Pcs Waterproof Plastic Tags Plastic Labeling Tags Shipping Label Tags with Reinforced Metal Holes Tear Resistant 15 Mil Blank Tags for Name Price Luggage Clothing Bag (Yellow,2 x 4)17 Jun 2024
Thyle 500 Pcs Waterproof Plastic Tags Plastic Labeling Tags Shipping Label Tags with Reinforced Metal Holes Tear Resistant 15 Mil Blank Tags for Name Price Luggage Clothing Bag (Yellow,2 x 4)17 Jun 2024 -
 Number Tags 1-100 Numbered Labeling Tags with Hole Easy Fastened 100PCS Plastic for Key Tags Identification Tags for Loc - AliExpress17 Jun 2024
Number Tags 1-100 Numbered Labeling Tags with Hole Easy Fastened 100PCS Plastic for Key Tags Identification Tags for Loc - AliExpress17 Jun 2024 -
 58,300+ Labeling Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock17 Jun 2024
58,300+ Labeling Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock17 Jun 2024 -
 Blank Heavy Duty 15 Mil Waterproof Plastic Tags - Equipment - Valve - Backpack - Pack of 100 (2 x 4, Dark Blue) : Office Products17 Jun 2024
Blank Heavy Duty 15 Mil Waterproof Plastic Tags - Equipment - Valve - Backpack - Pack of 100 (2 x 4, Dark Blue) : Office Products17 Jun 2024 -
 Price Tags & Labeling - Findings Outlet17 Jun 2024
Price Tags & Labeling - Findings Outlet17 Jun 2024 -
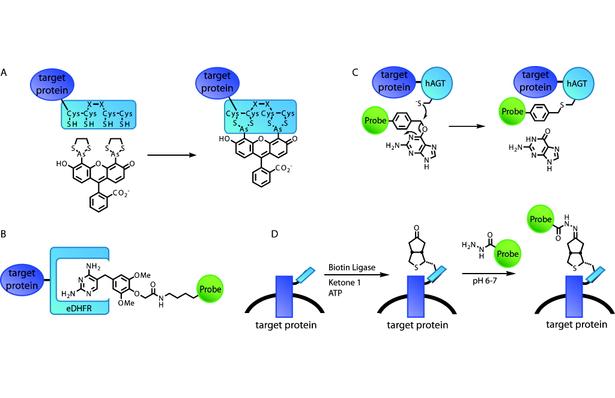 Chemical tags for labeling proteins inside living cells17 Jun 2024
Chemical tags for labeling proteins inside living cells17 Jun 2024 -
 Editable, Anywhere, Anything Classroom Decorative Tags for Labeling your Room17 Jun 2024
Editable, Anywhere, Anything Classroom Decorative Tags for Labeling your Room17 Jun 2024 -
 100 Plastic Tags Shipping Tags Water Proof Tags for17 Jun 2024
100 Plastic Tags Shipping Tags Water Proof Tags for17 Jun 2024
You may also like
-
 Jam Paper Industrial Bulk Wrapping Paper, 1/Pack, Glitter Birthday Gift Wrap, 1042.5 Sq ft (1/2 Ream), Size: 5004 x 3017 Jun 2024
Jam Paper Industrial Bulk Wrapping Paper, 1/Pack, Glitter Birthday Gift Wrap, 1042.5 Sq ft (1/2 Ream), Size: 5004 x 3017 Jun 2024 -
 STANLEY 33-886U-1-81 FatMax XTREME Super Metric Tape Measure Steel Tape Measure Measuring Ruler Metric Ruler Wear-resistant - AliExpress17 Jun 2024
STANLEY 33-886U-1-81 FatMax XTREME Super Metric Tape Measure Steel Tape Measure Measuring Ruler Metric Ruler Wear-resistant - AliExpress17 Jun 2024 -
 C-Lon Size D Beading Thread - 1 Bobbin - Sea Foam Green17 Jun 2024
C-Lon Size D Beading Thread - 1 Bobbin - Sea Foam Green17 Jun 2024 -
 ISeek Ser.: Fingerprint Fairies : (Kid's Activity Books, Art Books for Kids, Fairy Craft Books) by Insight Insight Kids (2021, Trade Paperback) for sale online17 Jun 2024
ISeek Ser.: Fingerprint Fairies : (Kid's Activity Books, Art Books for Kids, Fairy Craft Books) by Insight Insight Kids (2021, Trade Paperback) for sale online17 Jun 2024 -
 3M MASKING FILM17 Jun 2024
3M MASKING FILM17 Jun 2024 -
 Scrapbook Paper Cart, 12x12 Craft Paper Storage, Rolling Cart for Sale in Las Vegas, NV - OfferUp17 Jun 2024
Scrapbook Paper Cart, 12x12 Craft Paper Storage, Rolling Cart for Sale in Las Vegas, NV - OfferUp17 Jun 2024 -
 Scotch Double Sided Adhesive Tape Runner Permanent Refill, Photo Safe, 0.31 x 49 Feet (6055-R)17 Jun 2024
Scotch Double Sided Adhesive Tape Runner Permanent Refill, Photo Safe, 0.31 x 49 Feet (6055-R)17 Jun 2024 -
 ORLANDO FL POLICE PATCH OLD SCHOOL17 Jun 2024
ORLANDO FL POLICE PATCH OLD SCHOOL17 Jun 2024 -
 PME Sugar Pearls White17 Jun 2024
PME Sugar Pearls White17 Jun 2024 -
 Cricut Joy Smart Vinyl - Permanent Vinyl17 Jun 2024
Cricut Joy Smart Vinyl - Permanent Vinyl17 Jun 2024